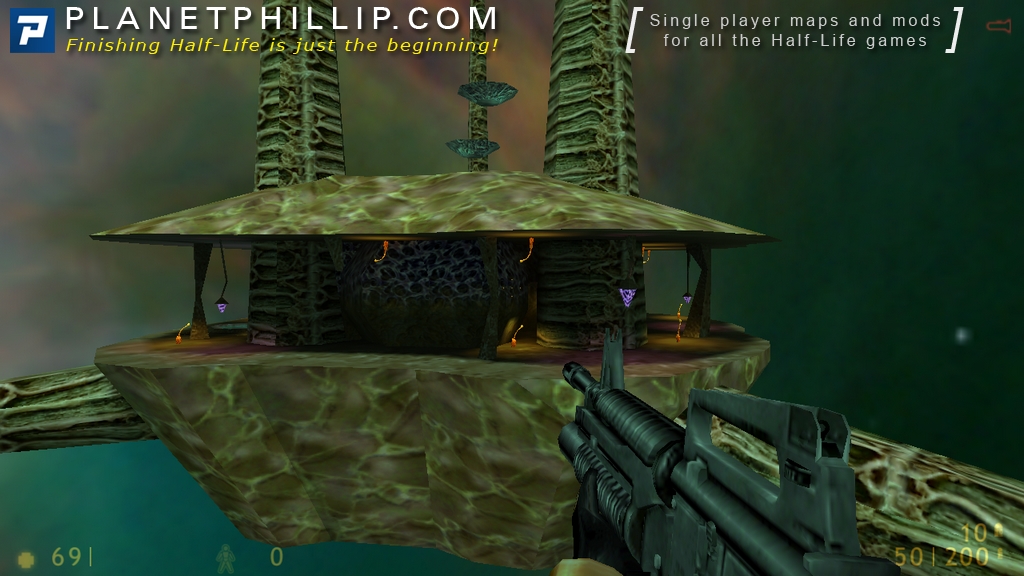
Half Life 1 Xen
Late last year, Crowbar Collective released the ending — a dramatic reworking of the infamous Xen levels, one of Half-Life's weakest areas.
. WW: February 14, 2013Mode(s),Half-Life is a game developed by and published by for in 1998. It was Valve's debut product and the first game in the. Players assume the role of, a scientist who must find his way out of the Black Mesa Research Facility after it is invaded by aliens. The core consists of fighting alien and human enemies with a variety of weapons and solving puzzles.Unlike many other games at the time, the player has almost uninterrupted control of Freeman, and the story is told mostly through seen through his eyes. Valve co-founder said the team aimed to create an immersive world rather than a 'shooting gallery'. They built Half-Life using, a heavily modified version of the, licensed from.Half-Life received acclaim for its graphics, realistic gameplay, and seamless narrative.
It won over fifty ' awards and is considered one of the most influential games of the first-person shooter genre, as well as one of the. By 2008, the game had sold over 9 million copies. It was followed by the (1999) and (2001).
It was ported to the in 2001, along with another expansion, and to and in 2013. Valve ported Half-Life to its engine in 2004, while a third-party remake, was released in 2020.Half-Life sparked numerous fan-made, several of them becoming standalone games, notably,. A sequel, was released in 2004, followed by, and in 2020. In this scene, the player must bypass a dam reservoir guarded by an attack helicopter, a squad of soldiers, and a gun emplacement.Half-Life is a that requires the player to perform combat tasks and puzzle solving to advance through the game.
Unlike most of its peers at the time, Half-Life used scripted sequences, such as a ramming down a door, to advance major plot points. Compared to most first-person shooters of the time, which relied on to detail their plotlines, Half-Life 's story is told mostly using scripted sequences (bar one short cutscene), keeping the player in control of the. In line with this, the player rarely loses the ability to control the, who never speaks and is never actually seen in the game; the player sees 'through his eyes' for the entire length of the game. Half-Life has no 'levels'; it instead divides the game into chapters, whose titles flash on the screen as the player moves through the game. Progress through the world is continuous, except for short pauses for loading.The game regularly integrates puzzles, such as navigating a maze of conveyor belts or using nearby boxes to build a small staircase to the next area the player must travel to. Some puzzles involve using the environment to kill an enemy, like turning a valve to spray hot steam at their enemies. There are few in the conventional sense, where the player defeats a superior opponent by direct confrontation.
Instead, such organisms occasionally define chapters, and the player is generally expected to use the terrain, rather than firepower, to kill the boss. Late in the game, the player receives a 'long jump module' for the, which allows the player to increase the horizontal distance and speed of jumps by crouching before jumping.
The player must rely on this ability to navigate various platformer-style in toward the end of the game.For the most part the player battles through the game alone, but is occasionally assisted by non-player characters; specifically security guards and scientists who help the player; the guards will fight alongside the player, and both guards and scientists can assist in reaching new areas and impart relevant plot information. An array of alien enemies populate the game, including,. The player also faces human opponents, in particular, Hazardous Environment Combat Unit (HECU) Marines and black ops assassins.Half-Life includes online multiplayer support for both individual and team-based modes. Plot Physicist arrives late for work at the.
He dons his Hazardous Environment Vehicle (HEV) suit to carry out an experiment; pushing an unusual material into a machine for analysis. During the experiment, the spectrometer explodes, creating a 'resonance cascade' that opens a portal to another dimension,. Surviving scientists urge Gordon to head to the surface, where he defends himself against hostile Xen creatures and government Marines sent to the incident.Heading to the surface, Gordon learns that scientists from the Lambda Complex may have found a way to close the portal. Gordon travels to the other end of the facility to assist them. Along the way, he activates a to destroy a giant tentacled creature and uses a disused railway system to reach and launch a satellite rocket. After he is captured by marines and left for dead in a garbage compactor, he escapes and makes his way to an older part of the facility.
There, he discovers Xen specimens collected before the incident. Overwhelmed by the aliens, the Marines pull out of Black Mesa and begin airstrikes. Scaling cliffs, navigating destroyed buildings, and traversing through underground water channels, Gordon arrives at the Lambda Complex, where scientists learn the portal is being forced open on the other side by an immensely powerful entity.
They have developed teleportation technology that allows Gordon to travel to Xen, where he is tasked to stop the entity.In Xen, Gordon encounters the remains of researchers before him and defeats Gonarch, a huge egg-laying headcrab. At a factory creating alien soldiers, he enters a portal that sends him to a vast cave. There, Gordon confronts the Nihilanth, the entity maintaining the rift, and destroys it. Gordon is summoned by the mysterious, who has been watching his progress in Black Mesa and praises him. The G-Man explains his 'employers' wish to employ Gordon. If Gordon refuses, he is teleported to an area full of alien soldiers to be killed immediately.
If Gordon accepts, the G-Man congratulates him and places him into stasis to await his task.Development. Main articles:, andTwo by outside developer Gearbox Software have been released for the PC version: (1999) and (2001). The former returns the player to Black Mesa during the events of Half-Life's storyline, but this time from the perspective of, one of the Marines in the sent to cover up evidence of the incident. It introduced several new weapons, new, both friendly and hostile and new, previously unseen areas of the facility.Blue Shift returns the player to Half-Life 's Black Mesa timeline once more, this time as, one of the facility's security guards. The expansion was initially developed as a bonus mission for the canceled Dreamcast version. Blue Shift came with the, that gave the player the option to update the look of Half-Life, Opposing Force, and the new Blue Shift content.Decay was another expansion by Gearbox, released only as an extra with the PlayStation 2 version of Half-Life.
The add-on featured co-operative gameplay in which two players could solve puzzles or fight against the many foes in the Half-Life universe.In 2000, a compilation pack, Half-Life: Platinum Pack, was released, including (with their respective manuals) Half-Life, Half-Life: Opposing Force. In 2002, the pack was re-released under the new titles Half-Life Platinum Collection and Half-Life: Generation. These new iterations also included the Half-Life: Blue Shift expansion pack; though if registered on, as well as and were also included. In 2005, Half-Life 1: Anthology was released, containing Steam-only versions of the following games on a single: Half-Life, Half-Life: Opposing Force, Half-Life: Blue Shift, and Team Fortress Classic. Remakes To experience firsthand the processes mod-makers would have to go through with the new engine, Valve Half-Life (dubbed Half-Life: Source) and Counter-Strike to their new. Half-Life: Source is a straight port, lacking any new content or the Blue Shift High Definition pack.
However, it does take advantage of for more realistic water effects, as well as Half-Life 2 's realistic physics engine. They also added several other features from Half-Life 2, including improved dynamic lightmaps, vertex maps, ragdolls, and a shadowmap system with cleaner, higher resolution, specular texture and normal maps, as well as utilization of the render-to-texture soft shadows found in Half-Life 2's Source engine, along with 3D replacements in place of the old 16-bit color prerendered bitmap skies. The Half-Life port possesses many of the Source engine's graphical strengths as well as control weaknesses that have been noted in the Source engine. Later updates added a option, support for OS X and Linux, an optional high-definition texture pack, among other improvements. Half-Life: Source is available with special editions of Half-Life 2, or separately on Steam. Half-Life Deathmatch: Source, the portion of the original game, much in the same fashion as the earlier released Half-Life: Source, was released in July 2005.Half-Life: Source had been criticized for not fully using many of the features of the Source engine found in Half-Life 2, as it still uses textures and models from the original game. In response to this, a third-party mod remake called was developed with Valve's approval.
Black Mesa, a fan-made remake of Half-Life utilizing the Source engine, began development in 2005 and was released as a free download on September 14, 2012, lacking only the final Xen chapter. The Xen portion was held back until December 2019 as the project team wanted to revamp this to try to address how the original Xen was poorly received compared to the rest of the game. The free 2007 Source SDK base is needed to run the game. Black Mesa is also distributed via Steam; the remake was among the first ten games whose release on the platform was approved using Valve's service. A separate effort, Project Lambda, is attempting to recreate Half-Life in the, allowing the game to support more advanced graphic features. Main articles:, andwas announced at 2003 and released in 2004. The player controls Freeman 20 years after the Black Mesa incident in the, where he joins a rebellion against an alien regime.
It was followed by two sequels, (2006) and (2007). Another sequel, was released in 2020. Reception Sales According to Newell, Half-Life was budgeted with the expectation of lifetime sales around 180,000 units. However, following its November 19 release, the game became a surprise hit. In the United States, Half-Life debuted at #8 on 's weekly computer game sales chart for the November 15–21 period, with an average retail price (ARP) of $49.
It rose to sixth place the following week, before dropping to position 10 for the week ending December 5. During the December 6–12 period, the game climbed back to sixth place; by this time, its ARP had dropped to $36. It placed between sixth and eighth on PC Data's weekly charts through the end of December, and its ARP rose back to $45 by the week ending January 2. PC Data declared Half-Life November's sixth-best-selling computer game in the United States, a position it held for the month of December.
While its US sales were below 100,000 copies by November 30, by 1999 it had sold 212,173 copies and earned revenues of $8.6 million in the United States by the end of 1998.In January 1999, Half-Life debuted at #3 on 's computer game sales rankings for the United Kingdom, and remained in PC Data's weekly top 10 for the entire month, peaking at #4. By January 19, after two full months of availability, global sales of Half-Life surpassed 500,000 units. In the United States, it was the fifth-best-selling computer game for the month of January. On PC Data's weekly charts, it rose to #2 from February 7–20, with an ARP of $35. Holding a position in the weekly top 10 for the rest of February, it climbed to fourth for the month.
The game remained in PC Data's weekly top 10 until the week of March 21 and dropped to position 11 for March as a whole. In the United Kingdom, it placed second in February—behind the debut of —and fifth in March. In April, it claimed #3 on Chart-Track's rankings and dropped to #16 on those of PC Data. On April 23, Sierra announced that global sales of Half-Life had reached almost 1 million copies.After maintaining the 16th place for May in the US, Half-Life exited PC Data's monthly top 20 in June. Half-Life became the fifth-bestselling computer game of the first half of 1999 in the US. Its domestic sales during 1999 reached 290,000 copies by the end of September. During 1999, it was the fifth best-selling computer game in the US, with sales of 445,123 copies.
These sales brought in revenues of $16.6 million, the sixth-highest gross that year for a computer game in the US. The following year, it was the 16th best-selling computer game in the US, selling another 286,593 copies and earning $8.98 million.The PlayStation 2 version received a 'Silver' sales award from the (ELSPA), indicating sales of at least 100,000 copies in the United Kingdom. Half-Life 's global sales reached 2.5 million units by July 2001. Noted in 2003 that 'a significant number of the 7.5m copies of the PC version were bought because the game offered such potential for community-driven expansion'. As of November 16, 2004, eight million copies of the game had been sold, by 2008, 9.3 million copies had been sold at retail. Awarded Half-Life the world record for Best-Selling First-Person Shooter of All Time (PC) in the Guinness World Records: Gamer's Edition 2008.Reviews ReceptionAggregate scoreAggregatorScore96/100 (PC)87/100 (PS2)Review scoresPublicationScore9.4/109.5/10(PC)(PS2)Half-Life has a score of 96 out of 100 on aggregate review website. 's said that the game 'is not just one of the best games of the year.
It's one of the best games of any year, an instant classic that is miles better than any of its immediate competition, and – in its single-player form – is the best shooter since the original '. Described it as 'a tour de force in game design, the definitive single player game in a first-person shooter'. Claimed that it was the 'closest thing to a revolutionary step the genre has ever taken'.reviewed the PC version of the game, rating it five stars out of five, and stated that 'It is fast paced, it is dramatic, and it brings the very idea of adventure on a PC out of the dark ages and into a 3D world. All that and not a single Orc in sight.' Several reviewers cited the level of immersion and interactivity as revolutionary. Said, 'It isn't everyday that you come across a game that totally revolutionizes an entire genre, but Half-Life has done just that.' Hot Games commented on the realism, and how the environment 'all adds up to a totally immersive gaming experience that makes everything else look quite shoddy in comparison'.
Gamers Depot found the game engaging, stating that they have 'yet to play a more immersive game period'. Said that Half-Life was an 'immersive and engaging entertainment experience', but noted that this only lasted for the first half of the game, explaining that the game 'peaked too soon'.The final portion of the game, taking place in the alien world of Xen, was generally considered the weakest. Besides introducing a wholly new and alien setting, it also featured a number of low-gravity jumping puzzles. The GoldSrc engine did not provide as much precise control for the player during jumping, making these jumps difficult and often with Freeman falling into a void and the player restarting the game.
's Julie Muncy called the Xen sequence 'an abbreviated, unpleasant stop on an alien world with bad platforming and a boss fight against what appeared, by all accounts, to be a giant floating infant'.During the 2nd Annual (now known as the D.I.C.E. Awards), Half-Life won the awards for 'Computer Game of the Year' and 'Computer Action Game of the Year', along with nominations for 'Game of the Year', 'Outstanding Achievement in Art/Graphics', 'Outstanding Achievement in Character or Story Development', 'Outstanding Achievement in Interactive Design' and 'Outstanding Achievement in Software Engineering'.Jeff Lundrigan reviewed the PlayStation 2 version of the game for, rating it three stars out of five, and stated that 'It may be getting old, but there's still a surprising amount of life in Half-Life.' In the November 1999, October 2001, and April 2005 issues of, Half-Life was named Best Game of All Time/Best PC Game Ever. In 2004, held a Title Fight, in which readers voted on what they thought was the greatest game of all time, and Half-Life was the overall winner of the survey.
Gave it their Quantum Leap Award in the FPS category in 2006. Inducted Half-Life into their Greatest Games of All Time list in May 2007.
In 2013, IGN described Half-Life as one of the most influential video games, saying that the history of the FPS genre 'breaks down pretty cleanly into pre- Half-Life and post- Half-Life eras'. Main articles:, andHalf-Life saw fervent support from independent game developers, due in no small part to support and encouragement from Valve., the level-design tool used during the game's development, was included with the game software. Printed materials accompanying the game indicated Worldcraft's eventual release as a retail product, but those plans never materialized. Valve also released a, enabling developers to modify the game and create. Both tools were significantly updated with the release of the 1.1.0.0. Supporting tools (including texture editors, model editors, and level editors such as the multiple engine editor ) were either created or updated to work with Half-Life.The Half-Life software development kit served as the development base for many multiplayer mods, including the Valve-developed Team Fortress Classic and Deathmatch Classic (a remake of Quake 's multiplayer deathmatch mode in the GoldSrc engine). Other mods such as Counter-Strike and ( DOD) began life as the work of independent developers (self-termed 'modders') who later received aid from Valve.
Other multiplayer mods include, and.Numerous single-player mods have also been created. Notable examples include (1999, a futuristic action-adventure on board a zoological research spaceship), (2000–2001, a trilogy involving zombies), (2001, a follow-up to the original Half-Life story with improved graphics), and (2002, a side-story to the original Half-Life).In 2003, Valve's network was infiltrated by hackers. Among the files that were stolen included an unreleased Half-Life modification: Half-Life: Threewave, a canceled remake of the mod from Quake. The files were later found by independent reporter Tyler McVicker of Valve News Network on a Vietnamese in February 2016, and were unofficially released to the public in September 2016.Some Half-Life modifications eventually landed on retail shelves. Counter-Strike was the most successful, having been released in six different editions: as a standalone product (2000), as part of the Platinum Pack (2000), as an version (2003), and as a single-player spin-off titled (2004), as well as in two versions using the Source engine.
Team Fortress Classic, Day of Defeat, (2000, a futuristic -style with emphasis on its single-player mode) and Sven Co-op were also released as standalone products.In addition to mods, Half-Life was also the subject of the series Half-Life VR but the AI is Self-Aware and Freeman's Mind. References. 'Reviews.
Half-Life'. December 1998. From the original on November 26, 2007. Retrieved April 25, 2007. ^ Bell, Joe Grant (November 25, 1998). Half-Life: Prima's Official Strategy Guide.
Tufnell, Nicholas (November 25, 2011). The Cambridge Student Online. Archived from on November 26, 2011. Retrieved November 26, 2011. ^. Archived from on May 20, 2012.
Retrieved September 12, 2006. Archived from on February 23, 2011. Retrieved September 12, 2006. ^ Hodgson, David (2004). Half-Life 2: Raising the Bar.
Prima Games. ^. Archived from on February 24, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2006. (in Spanish).
August 29, 2018. Archived from on February 24, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2006. Archived from on March 8, 2010. Retrieved September 14, 2006. Pp. 106–7.
^ Birdwell, Ken (December 10, 1999). From the original on November 16, 2016.
Retrieved February 14, 2017. ^.
Archived from on September 28, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2006. ^. Arcade Attack.
July 17, 2017. Retrieved November 23, 2019. Wawro, Alex (February 13, 2017). From the original on February 14, 2017.
Retrieved February 13, 2017. Archived from on February 25, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2006. Retrieved March 19, 2019. IGN Staff (February 11, 1999).
Combine OverWiki (January 2, 2011), retrieved March 24, 2019. Frank, Allegra (May 4, 2017).
Retrieved March 22, 2019. Stahl, Ben (September 5, 2000). Retrieved October 26, 2008. ^ Chau, Anthony (June 18, 2001).
From the original on August 4, 2016. Retrieved July 18, 2016. IGN Staff (March 29, 2001). From the original on August 20, 2016. Retrieved July 18, 2016. November 17, 2000.
Ostergrad, Genevieve (April 23, 1999). Archived from on February 23, 2012. Retrieved July 18, 2016. alfred (January 29, 2013). From the original on August 14, 2016.
Retrieved July 18, 2016. alfred (February 14, 2013).
From the original on August 14, 2016. Retrieved July 18, 2016. Archived from on March 24, 2019. Retrieved March 24, 2019. CS1 maint: archived copy as title. Archived from on December 19, 2015. Retrieved March 24, 2019.

CS1 maint: archived copy as title. Retrieved March 24, 2019. September 25, 2013.
From the original on March 20, 2015. Retrieved March 9, 2015. Harris, Wil (September 18, 2004). Archived from on June 4, 2008. Retrieved March 27, 2008. Retrieved March 22, 2019.
Kelly, Andy (November 2, 2017). Retrieved September 16, 2018. Grayson, Nathan (May 9, 2012).
From the original on September 8, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2012. Senior, Tom (September 3, 2012). From the original on September 22, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2012. Cobbett, Richard (September 14, 2012).
From the original on September 25, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2012. September 3, 2012. Retrieved September 3, 2012. McWhertor, Michael (December 22, 2016).
Retrieved December 22, 2016. September 11, 2012. From the original on September 18, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2012.
Plunkett, Luke (September 16, 2018). Retrieved September 16, 2018. Thorsen, Tor (May 24, 2006). From the original on November 25, 2013. Retrieved April 27, 2007.
Hollister, Sean (November 21, 2019). Retrieved November 24, 2019. ^ Baker, M. Sharon (February 26, 1999). Archived from on February 19, 2003.
^ Biederman, Christine (January 14, 1999). Archived from on October 3, 2012. Mayer, Robert (December 9, 1998). Archived from on April 6, 2005. Retrieved July 22, 2018. December 9, 1998. Archived from on June 14, 2000.
Retrieved July 22, 2018. December 15, 1998. Archived from on June 21, 2000. Retrieved July 22, 2018. December 22, 1998. Archived from on June 6, 2000.
Retrieved July 22, 2018. Fudge, James (January 8, 1999). Archived from on April 7, 2005. Retrieved July 22, 2018. January 8, 1999. Archived from on March 11, 2000.
Retrieved July 22, 2018. ^ Mullen, Micheal (January 12, 1999).
Archived from on February 29, 2000. Retrieved July 22, 2018. Mayer, Robert (December 13, 1998). Archived from on April 6, 2005. Retrieved July 2, 2018. Ocampo, Jason (January 15, 1999). Archived from on May 2, 2005.
Retrieved July 22, 2018. 'The Numbers Game'. April 1999. McNicholas, Conor (February 1999). 'Charts; The ChartTrack Top 10'. (73): 30. Fudge, James (January 19, 1999).
Archived from on April 6, 2005. Retrieved July 22, 2018. January 27, 1999. Archived from on March 8, 2000. Retrieved July 22, 2018. February 2, 1999. Archived from on February 26, 2000.
Retrieved July 22, 2018. February 9, 1999. Archived from on March 8, 2000.
Retrieved July 22, 2018. February 18, 1999. Archived from on February 29, 2000. Retrieved July 22, 2018. Mullen, Micheal (February 16, 1999). Archived from on June 7, 2000. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
Bosch serial number location drill. Model #: 32614.
Fudge, James (February 23, 1999). Archived from on April 7, 2005. Retrieved July 22, 2018. ^. March 10, 1999.
Archived from on November 19, 2000. Retrieved July 22, 2018. March 16, 1999. Archived from on March 3, 2000.
Retrieved July 22, 2018. March 15, 1999. Archived from on November 8, 1999. Retrieved July 22, 2018. March 25, 1999.
Archived from on June 3, 2000. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
April 5, 1999. Archived from on June 19, 2000. Retrieved July 22, 2018. Fudge, James (April 16, 1999). Archived from on April 7, 2005. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
Shoemaker, Richie (March 1999). 'Charts; The ChartTrack Top 10'. (74): 74. ^ Shoemaker, Richie (May 1999). 'Charts; The ChartTrack Top 10'. (76): 26. Fudge, James (May 17, 1999).
Archived from on May 2, 2005. Retrieved July 22, 2018. (Press release).:. April 23, 1999. Archived from on October 9, 1999. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
Fudge, James (June 15, 1999). Archived from on May 2, 2005. Retrieved May 8, 2018. Fudge, James (July 20, 1999). Archived from on April 7, 2005. Retrieved May 8, 2018.
IGN Staff (August 3, 1999). Archived from on March 5, 2000. Retrieved July 22, 2018. 'X-Tra; Death of the PC'. (18): 100, 101.
February 2000. Fudge, James (January 19, 2000). Archived from on August 17, 2000. 'Shake Your Money-Maker'.
April 2000. Archived from on February 21, 2009.
Caoili, Eric (November 26, 2008). Archived from on September 18, 2017. Price, Tom (July 2001).
'Army of One'. (204): 50–55.
'Prescreen focus: Half-Life 2'. (124): 48–53. June 2003.
Mike Musgrove (November 16, 2004). Washington Post. From the original on October 25, 2012.
Retrieved February 28, 2008. (December 3, 2008). Archived from on December 21, 2008. From the original on February 2, 2017. Retrieved November 3, 2011. From the original on December 3, 2011. Retrieved November 3, 2011.
^ House, Michael L. Archived from on November 14, 2014. ^ Green, Jeff (February 1, 1999). Archived from on February 9, 2002.
Retrieved April 14, 2010. ^.
From the original on October 31, 2013. Retrieved April 25, 2007. ^ 'Finals'.
February 1999. Mendelian genetics study guide. Pp. 94–95. ^ Lundrigan, Jeff (December 2001). Vol. 4 no. 12. Archived from on February 1, 2003. Retrieved March 30, 2008.
Gamers Depot. Archived from on March 8, 2005. Retrieved March 30, 2008. Archived from on September 10, 2007. Retrieved March 30, 2008. Hollerman, Patrick (2018).
'The Platform Theme'. Reverse Design. Hall, Charlie (November 19, 2018). Retrieved February 23, 2020. Muncy, Julie (March 5, 2020). Retrieved March 5, 2020.
Retrieved April 10, 2020. Archived from on May 23, 2010. Retrieved February 22, 2008. Archived from on May 11, 2013.
Retrieved September 3, 2006. Rorie, Matthew (May 18, 2007). From the original on January 19, 2015.
Retrieved March 31, 2016. From the original on March 12, 2017. Retrieved January 6, 2008. September 13, 2013. From the original on February 28, 2014. Retrieved February 23, 2014. Walker, Trey (June 7, 2001).
From the original on October 22, 2016. Orland, Kyle (September 21, 2016). Ars Technica. From the original on September 22, 2016. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
Zwiezen, Zack (April 19, 2020). Retrieved April 28, 2020. Staff, Ars (April 16, 2020). Ars Technica. Retrieved April 28, 2020. Livingston, Christopher (April 2, 2017). Retrieved April 28, 2020.External links Wikiquote has quotations related to:.
(archived).